CO2 mineralization in gas scrubbers using basalt slurries

Motivation
- BMBF:
5-15 % of current greenhouse gas emissions are unavoidable - IPCC:
Negative emissions are needed to limit the rise in temperature - Leopldina:
To achieve greenhouse gas neutrality, ... emissions ... must be offset by removing CO2 from the atmosphere - Global emissions currently just under 40 Gt per year
Removal of at least 4 Gt per year is required in the long term
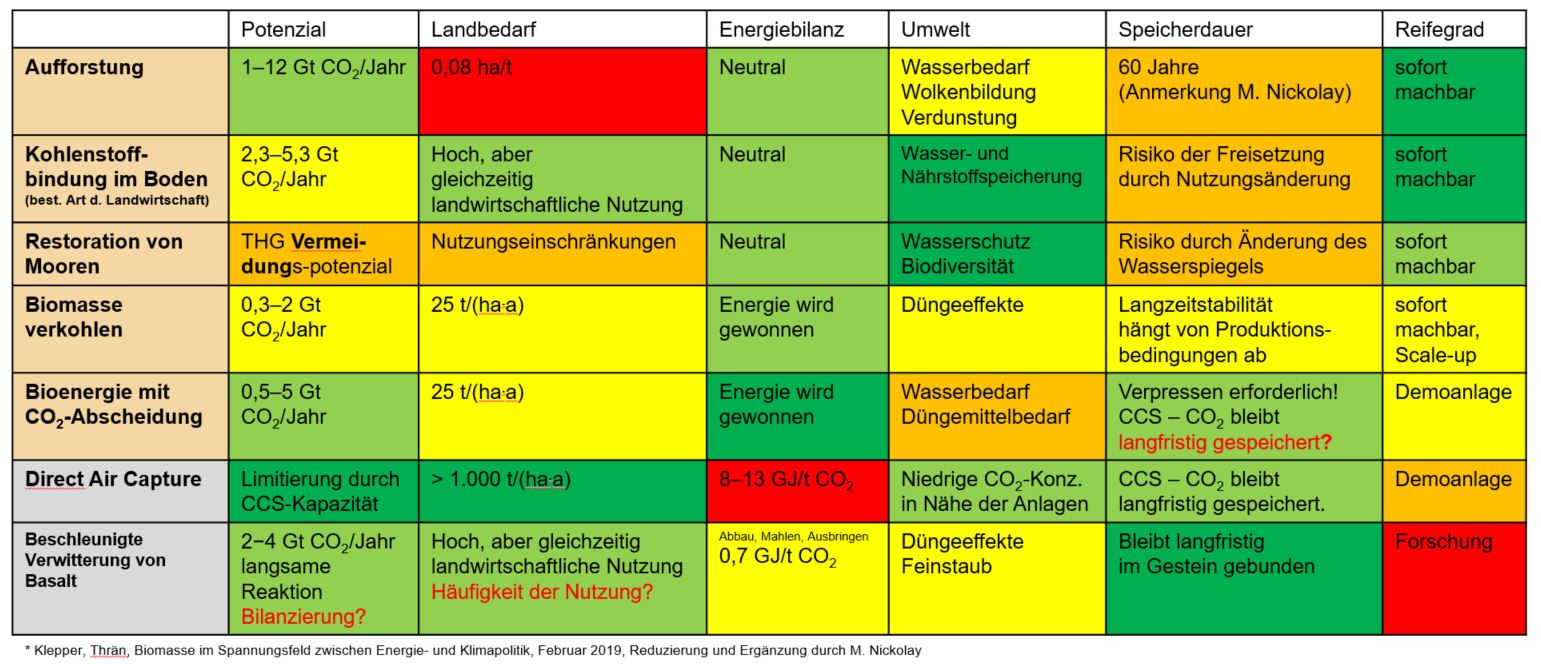
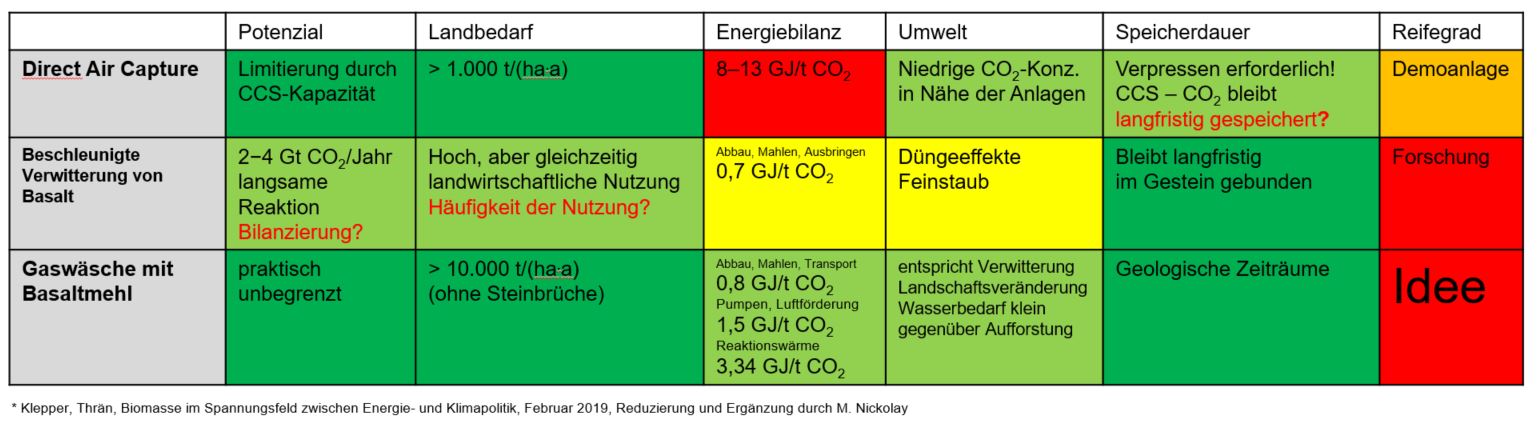
Options
Idea
Combination of Direct Air Capture and Accelerated Weathering in a gas scrubber using basalt slurry
Idea/potential
- Basalt is the most common rock in the Earth's mantle
- Basalt typically contains
10 mass % calcium oxide (CaO) and
10 mass % magnesium oxide (MgO) - CaO and MgO react with CO2 to form calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and magnesium carbonate (MgCO3)
- 1 ton of basalt absorbs 188 kg of CO2 as carbonates or
- 376 kg as dissolved hydrogen carbonates Hydrogen carbonates only exist in aqueous solution and are not to be considered for CO2 storage
Preliminary work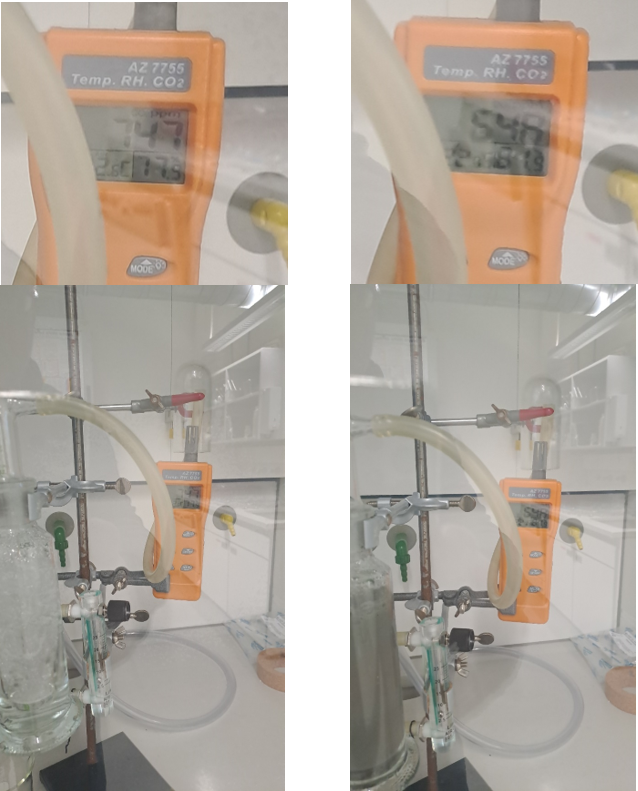
- Qualitative experiments with wash bottle
- Wash bottle 250 ml
- Sludge 30 %
- 2.5 l/min air 747 ppm 548 ppm > 15 min - Literature research
- Calculations
- Preparation of patent specification
- Development of test apparatus
Idea/execution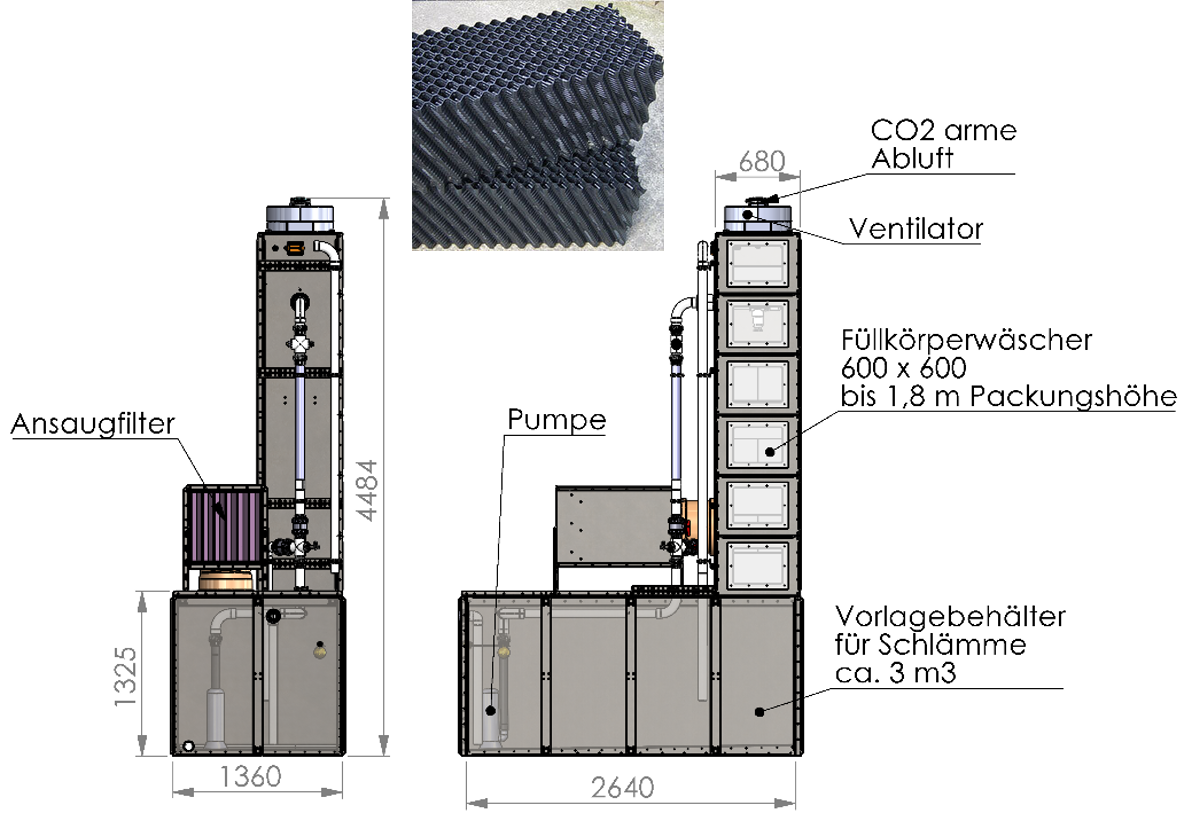
- Mining and crushing basalt
- Grind basalt to 50 µm
- Transport basalt to the gas scrubber
- Prepare 30 % basalt powder slurry
z. B.: 230 kg basalt + 770 kg water (+ 27 kg table salt) - Batch operation
Pump the sludge in the scrubber with air supply until the pH stops falling - Dewater and dispose of sludge
Yield/kinetics
- What determines the speed?
- Mass transfer of CO2 from air to water
- Diffusion in the water to the grain boundary
- Diffusion in the grain
- Dissolution of CaO/MgO in water
- Reaction between CaO/MgO and CO2
- Waking up of carbonate layers on the grain
- Degree of grinding
- Composition of the basalt
- Temperature - In the absence of knowledge:
Mass transfer of CO2 from air to water
Measurement of CO2 capture
- Measure air volume flow and CO2 concentration at the inlet and outlet (also records hydrogen carbonates)
- Gravimetric
Raw material
- Drying up to 200 °C weighing, firing > 850 °C weighing
- Mass difference equal to containedCO2
Reacted sludge
- Drying up to 200 °C weighing, firing > 850 °C weighing
- Mass difference equal to contained + absorbed CO2 - Alternative to firing: Expel the CO2 with hydrochloric acid
- Wet chemical
Raw material
- Dry to 200 °C, dissolve and titrate with hydrochloric acid above pH 8.3 to pH 4.3
Reacted sludge
- Dry to 200 °C, dissolve and titrate with hydrochloric acid over pH 8.3 to pH 4.3
Difference gives the absorbed CO2 - IR spectroscopy